As autonomous vehicles continue to evolve, their ability to see, think, and respond to complex environments relies on one critical capability: sensor fusion. Technologies such as cameras, LiDAR, radar, and ultrasonic sensors must work together seamlessly to ensure safety, accuracy, and reliability on the road. At the core of this process lies embedded system design, which enables real-time data processing, communication, and control of the true intelligence behind self-driving cars.
In this blog, we’ll explore how embedded systems make sensor fusion possible, the key design challenges, and how advanced design solutions are driving the next generation of autonomous vehicles.
Understanding Sensor Fusion in Autonomous Vehicles
Sensor fusion refers to the integration of multiple sensor inputs to form a single, unified perception of the environment. Each sensor type brings unique strengths:
- Cameras deliver rich visual details and color recognition.
- LiDAR provides accurate 3D mapping and depth perception.
- Radar detects object velocity and performs well in poor weather.
- Ultrasonic sensors assist in short-range proximity detection.
By combining data from these sensors, vehicles can identify objects, track motion, and predict behavior with far greater accuracy. However, processing massive amounts of data in milliseconds requires robust computing platforms; this is where embedded system design becomes essential.
How Embedded Systems Enable Sensor Fusion
Embedded systems are purpose-built computing units designed for real-time performance and reliability in constrained environments. In autonomous vehicles, they perform tasks such as:
- Acquiring and synchronizing data from multiple sensors
- Filtering and preprocessing raw signals
- Running sensor fusion algorithms and machine learning models
- Managing communication between sensors, actuators, and control systems
These systems must handle gigabytes of data per second, all while maintaining low latency and ensuring functional safety. Implementing such capabilities demands advanced design solutions that balance computing power, efficiency, and safety certifications like ISO 26262.
Key Functions of Embedded Systems in Fusion Pipelines
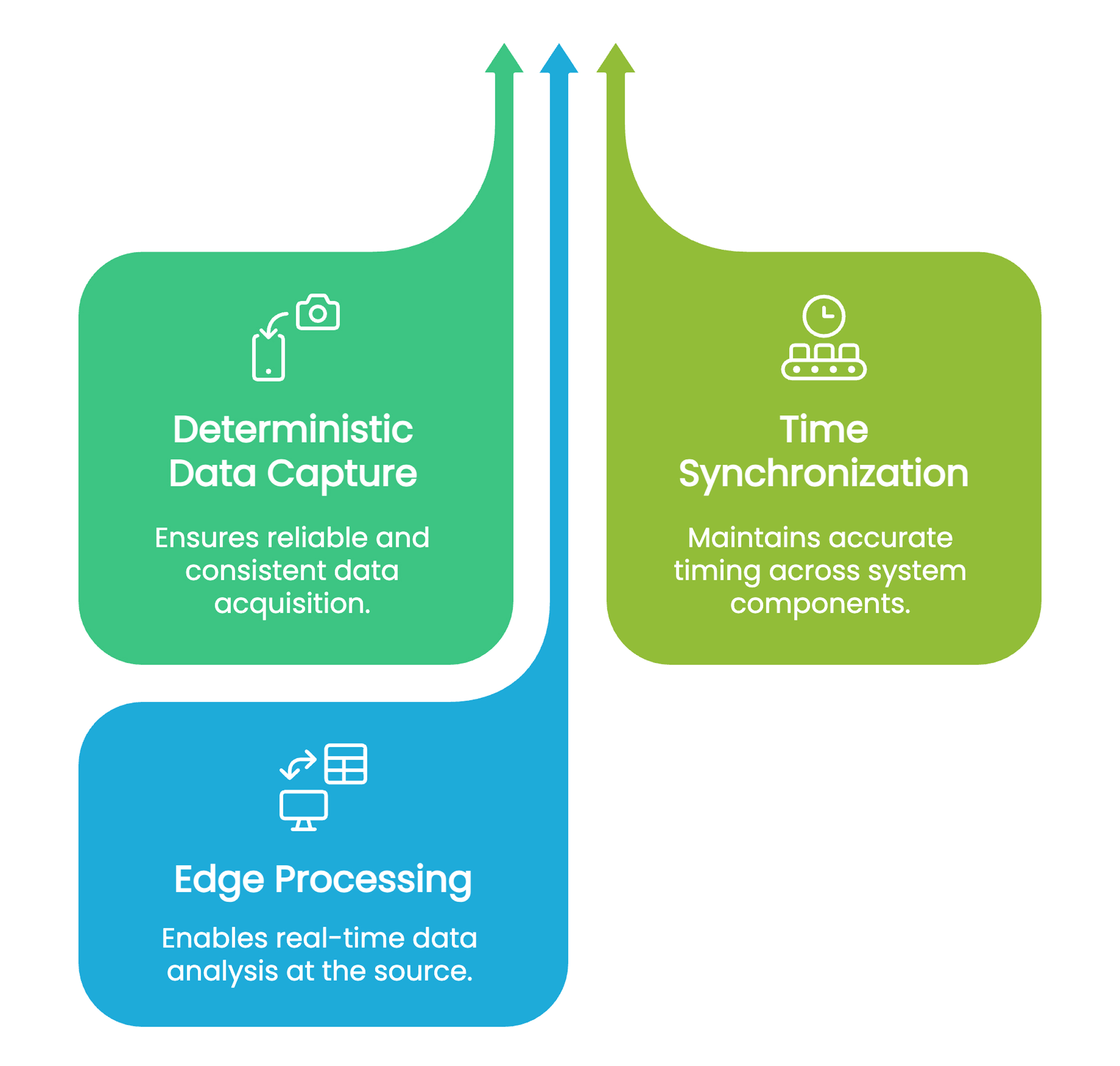
1. Deterministic Data Capture: Embedded systems ensure every data frame is captured without loss, using specialized interfaces and DMA pipelines.
2. Time Synchronization: Accurate timestamping aligns inputs from various sensors to a common timeline, using standards like IEEE 1588 Precision Time Protocol (PTP).
3. Edge Processing: To minimize delay, AI models are deployed directly on embedded hardware for on-the-fly object detection and classification.
This tight integration of software and hardware reflects the sophistication required in designing embedded system architectures for autonomous driving.
Managing Latency and Real-Time Constraints
Autonomous vehicles operate under strict timing requirements. A delay of even a few milliseconds can impact safety decisions. Engineers must decide:
- Which functions run on real-time microcontrollers
- Which tasks use dedicated GPUs or NPUs
- How data pipelines can be optimized to reduce copying and latency
Such challenges are addressed through advanced design solutions like deterministic scheduling, zero-copy buffers, and efficient data routing. Success depends on an engineer’s mastery of embedded system design, ensuring real-time reliability and predictable behavior under all conditions.
Hardware–Software Co-Design: Balancing Accuracy and Efficiency
Sensor fusion algorithms often trade accuracy for performance. For instance:
- High-precision deep learning models need powerful GPUs, but this increases power consumption.
- Simplified models on microcontrollers save power but may miss subtle environmental cues.
Achieving optimal results requires designing embedded system solutions through hardware–software co-design. Techniques include:
- Using FPGAs for pre-processing and deterministic computation
- Deploying AI accelerators for efficient neural inference
- Profiling workloads to balance compute and thermal constraints
This integration ensures the fusion pipeline meets both safety and performance objectives.
Trends in Embedded AI: Designing Hardware for Machine Learning on the Edge
Safety, Validation, and Testing in Embedded Systems
Automotive safety standards demand exhaustive validation under diverse real-world conditions. Embedded platforms must support:
- Comprehensive telemetry and logging for traceability
- Fail-safe operations to maintain control during sensor faults
- Secure boot and OTA updates to protect software integrity
Developing and validating these capabilities is itself an advanced design solution. It requires Hardware-in-the-Loop (HIL) simulations, automated testing, and lifecycle management, areas where deep expertise in embedded system design is critical.
Ecosystem and Tool Integration
Modern autonomous systems rely on an integrated ecosystem of tools and standards, such as:
- Middleware (ROS, DDS)
- Automotive networks (CAN, Ethernet AVB)
- Real-time operating systems (RTOS)
Expert engineers in designing embedded system architectures ensure these elements work seamlessly, maintaining deterministic performance while enabling flexibility for future updates.
Centralized vs. Distributed Fusion Architectures
Autonomous vehicles typically adopt one of three fusion models:
- Centralized Fusion: A single high-performance unit processes all sensor data.
- Distributed Fusion: Each domain controller (ADAS, powertrain, etc.) handles local fusion tasks.
- Hybrid Fusion: Combines both approaches, local edge fusion plus centralized global fusion.
Each model requires unique embedded system design approaches for redundancy, thermal efficiency, and real-time synchronization.
Partnering for Innovation in Sensor Fusion
Sensor fusion development involves multiple disciplines, such as hardware, firmware, AI algorithms, safety validation, and test engineering. To accelerate development and ensure compliance, many automotive companies collaborate with specialized engineering service providers who bring expertise, tools, and end-to-end validation environments.
Tessolve: Powering Innovation in Embedded and Automotive Systems
At Tessolve, we believe that the foundation of safe and intelligent autonomous vehicles lies in precision-engineered embedded systems. As a global engineering services leader, we specialize in complete embedded system design, from concept to validation. Our offerings span SoC and PCB development, firmware and FPGA design, and automotive-grade software integration.
We deliver advanced design solutions tailored for ADAS, autonomous systems, and in-vehicle networking, backed by cutting-edge labs for Hardware-in-the-Loop (HIL) and sensor validation testing. With deep domain expertise in safety standards, connectivity, and edge AI, Tessolve enables OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers to innovate faster and smarter.
By partnering with Tessolve, automotive teams can seamlessly design embedded system architectures that transform complex sensor-fusion concepts into production-ready, high-reliability systems, driving the future of autonomous mobility.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is sensor fusion in autonomous vehicles?
Sensor fusion combines data from multiple sensors to create a unified, accurate view of the driving environment for safer decisions.
Why is embedded system design crucial for sensor fusion?
It ensures real-time data processing, synchronization, and decision-making, which are essential for the safe operation of autonomous vehicles.
How do embedded systems enhance vehicle safety?
They provide redundancy, fault tolerance, and precise response timing, reducing the risk of errors or system failures during driving.
What role do embedded systems play in AI-powered perception?
They enable edge-level AI processing, allowing faster detection, object recognition, and response without relying solely on cloud or central computing.
